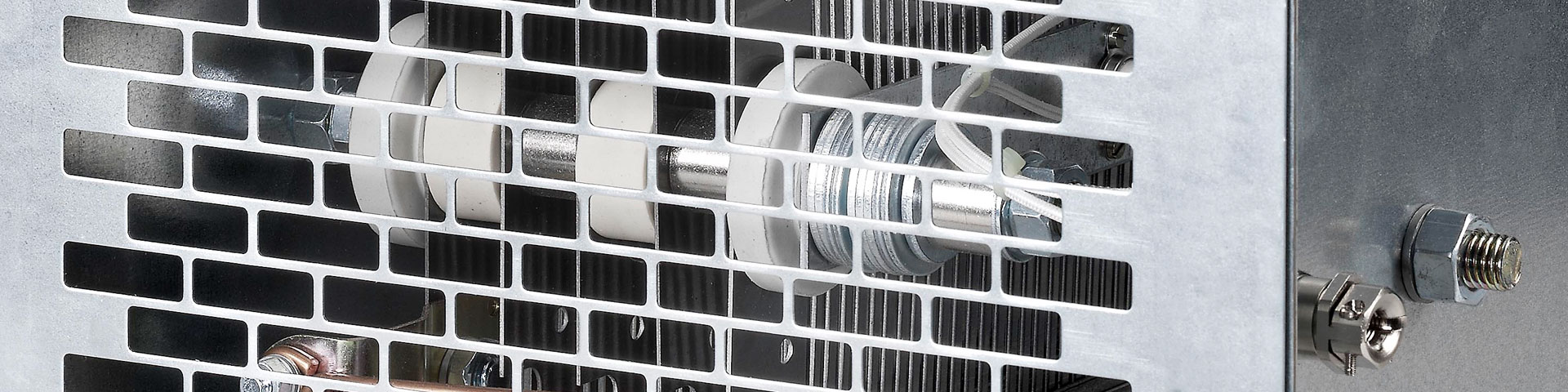
Oil-cooled or oil-immersed resistors are resistor units installed in transformer oil. The oil serves as a coolant, insulator and heat carrier. The heat transferred from the resistor to the oil is about 10 times higher than that to air. Oil-cooled resistors store large amounts of energy in the cooling fluid at low cost. Due to the good insulation properties of the oil smaller minimum spacing and creepage distances at higher voltages are possible in the oil than in air. The disadvantage is that the heat is transmitted very slowly to the tank wall, which is mostly small in relation to the storage capacity. Another disadvantage is the environmental hazard due to oil spillage in case of leakage. Oil ages with time and absorbs humidity, which affects its insulating properties.